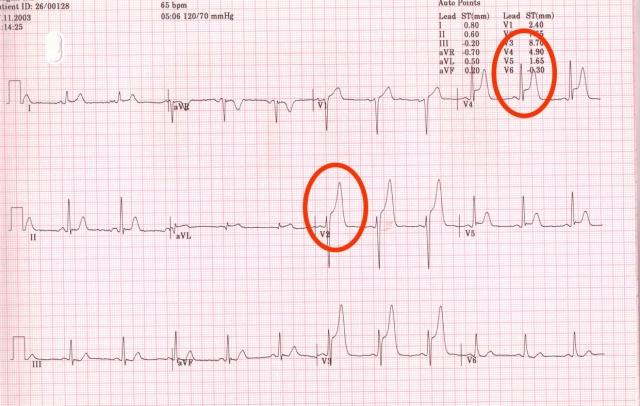
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Edinburgh found firefighters exposed to extremely high heat experienced elevated core body temperatures for up to four hours after exposure and their blood became “stickier” and more likely to form clots.